態 Stroke Order
Animated Stroke Order of 態
Stroke Order Diagrams for 態
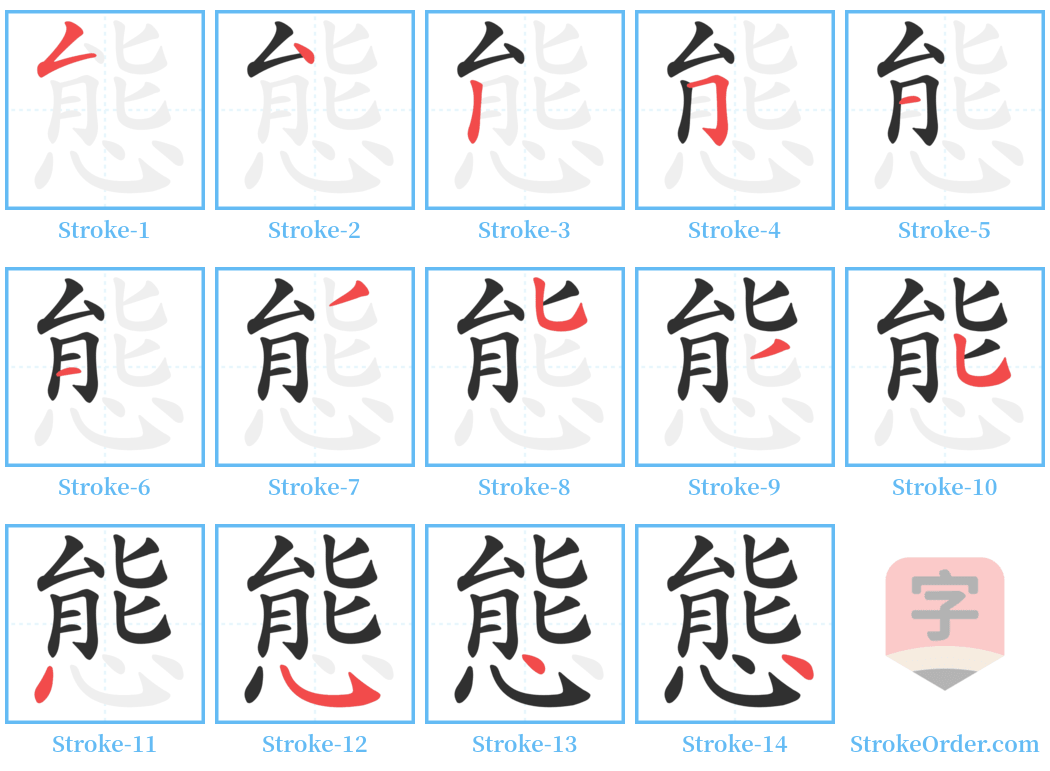
Step-by-Step Handwriting Guide for 態
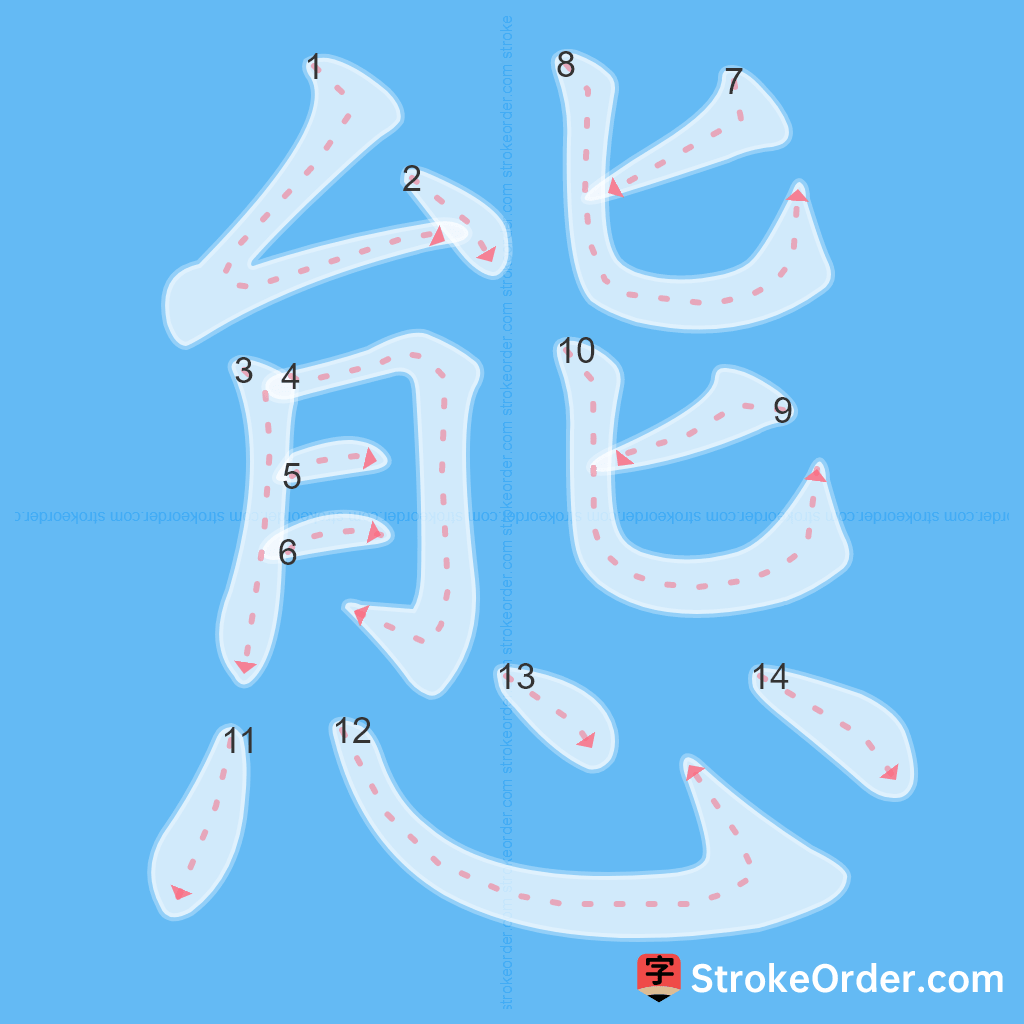
Learn to Write Chinese Characters with Video Tutorials
Watch the video of writing the Chinese character "態", learn the correct stroke order (笔顺) of the character "態", and master the standard way of writing the character "態".
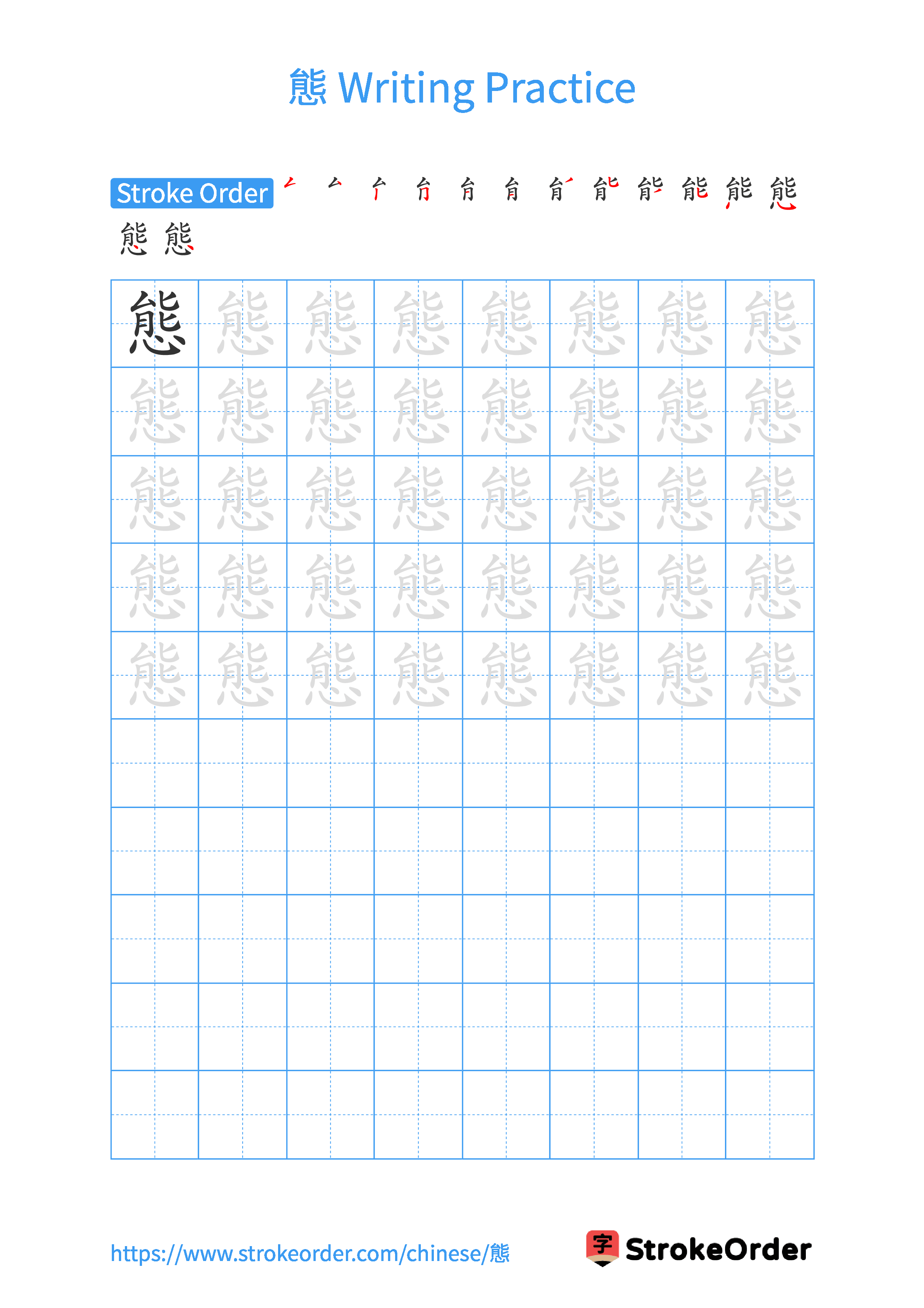
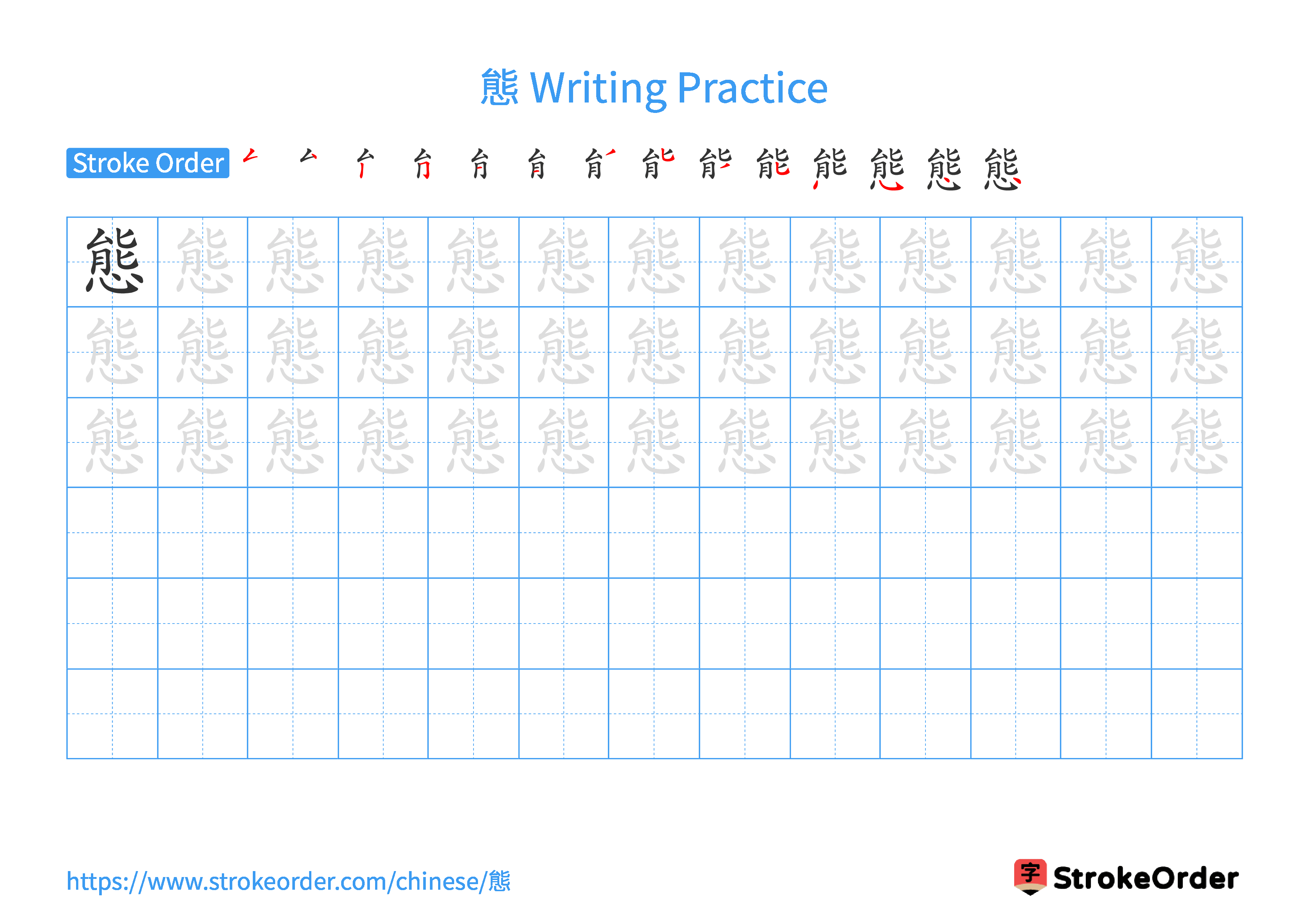
Free Printable Handwriting Practice with Stroke Order: 態
Printable Writing Practice Worksheet of "態" in Portrait Orientation (Tian Zi Ge)
Printable Writing Practice Worksheet of "態" in Landscape Orientation (Tian Zi Ge)
Information of 態
Pinyin
tài
Radical
心
Strokes
14 strokes
Usage
★★★
Definition
attitude
態
1. Spirit; posture; disposition.
- Example: 《說文•心部》: "態,意態也。" (Attitude refers to one's spirit and posture.)
- Comment: "意態者,有是意因有是狀,故曰意態。" (One's idea is formed due to one’s posture, hence the term attitude.)
- Example: 《楚辭•招魂》: "容態好比,順彌代些。" (The appearance of one’s demeanor is lovely and harmonious.)
- Comment: "態,姿也。" (Posture also refers to demeanor.)
- Example: 《史記•老子韓非列傳》: "態色與淫志,是皆無益於子之身。" (Posture and lascivious desires are of no benefit to one’s self.)
- Comment: "姿態之容色與淫欲之志皆無益於夫子,須去除也。" (The appearance and lascivious desires do not benefit the sage and should be eliminated.)
- Example: 唐崔顥《岐王席觀妓》: "還將歌舞態,只擬奉君王。" (The postures in singing and dancing are meant for the king.)
- Example: 宋陸游《秋思三首》之二: "山晴更覺雲含態,風定閑看水弄姿。" (On a clear mountain day, the clouds appear gentle; with still winds, water dances gracefully.)
2. Condition; attitude.
- Example: 《楚辭•離騷》: "寧溘死以流亡兮,余不忍為此態也。" (I would rather die than live in this condition.)
- Example: 《淮南子•主術》: "是以上多故則下多詐,上多事則下多態,上煩擾則下不定。" (When those above cause many issues, those below are often deceptive; when those above are preoccupied, those below become unstable.)
- Example: 《漢書•鄭當時傳》: "一貧一富,乃知交態。" (In wealth and poverty, one understands the condition of friendship.)
3. Elegance.
- Example: 北周庾信《趙國公集序》: "柱國趙國公,發言為論,下筆成章,逸態横生,新情振起。" (The Duke of Zhao is eloquent; his words become compositions, his elegance emanates, and new emotions arise.)
词性: 名词 情状。
- Example phrases: "事态" (situation), "形态" (form), "姿态" (posture).
词性: 名词
In grammar, it refers to the relationship between an action and its subject expressed through specific grammatical forms. Generally, it is divided into two types:
- Active voice: Action is initiated by the subject.
- Example phrase: "他玩球。" (He plays ball.)
- Passive voice: Action is received by the subject.
- Example phrase: "球被他玩。" (The ball is played by him.)
The passive voice in Chinese is often expressed with particles like "被", "给", etc.