缼 Stroke Order
Animated Stroke Order of 缼
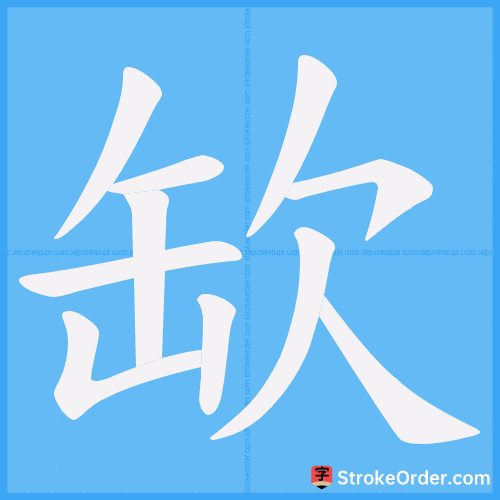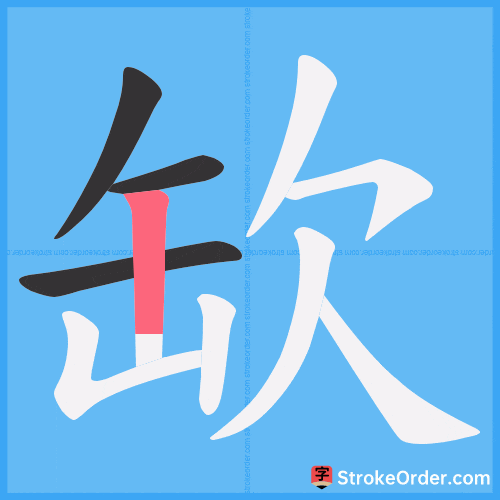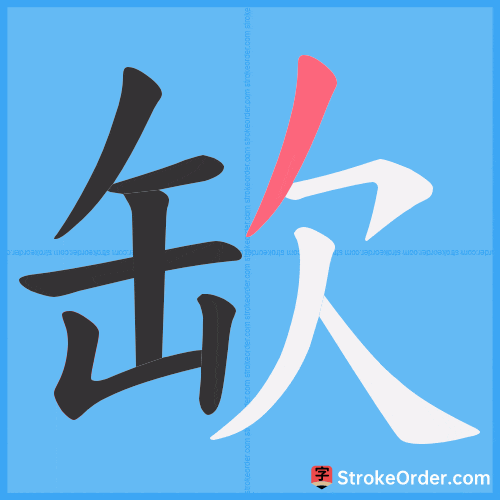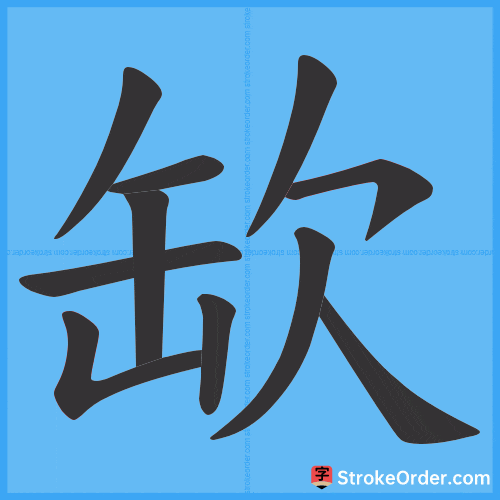
Stroke Order Diagrams for 缼
Information of 缼
Pinyin
quē
Radical
缶
Strokes
10 strokes
Usage
★★
Definition
缼:
1. Same as "缺" (quē), meaning to lack or be incomplete.
Example: The broken pottery or container serves as a model for "缺". The original meaning is: the damage to an object. It extends to mean lacking and incomplete. "缺" refers to the breaking of an object. — "Shuōwén"
2. Shortage; deficiency.
Example: "缺王道之仪." — "Hanshu · Sima Xiangru Zhuan"
Example: "于此微缺然." — Qing Dynasty, Yuan Mei, "祭妹文"
3. Gap; opening.
Example: "锋口为缺." — Qing Dynasty, Shao Changheng, "青门剩稿"
4. Defect. It extends to mean a regret or limitation.
Example: "犹欲保残守缺." — "Wenxuan · Liu Xin · 移太常博士书"
5. In the dialect of Henan, "缺" represents the meaning of deception or cheating.