焉 Stroke Order
Animated Stroke Order of 焉

Stroke Order Diagrams for 焉
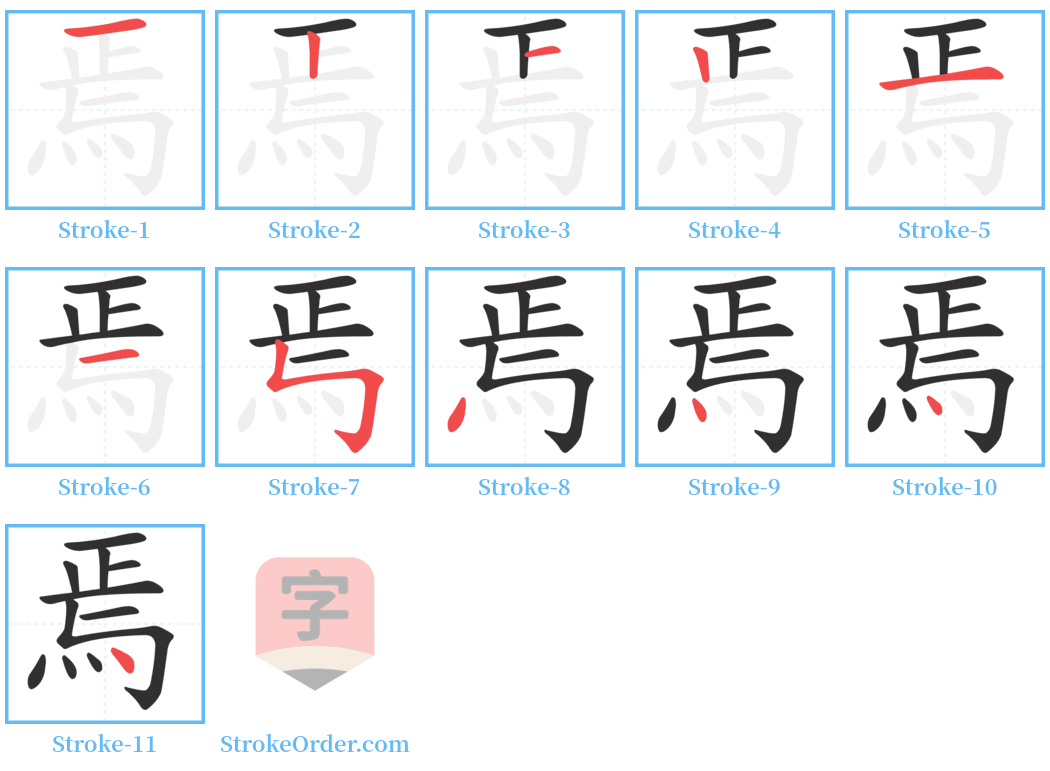
Step-by-Step Handwriting Guide for 焉
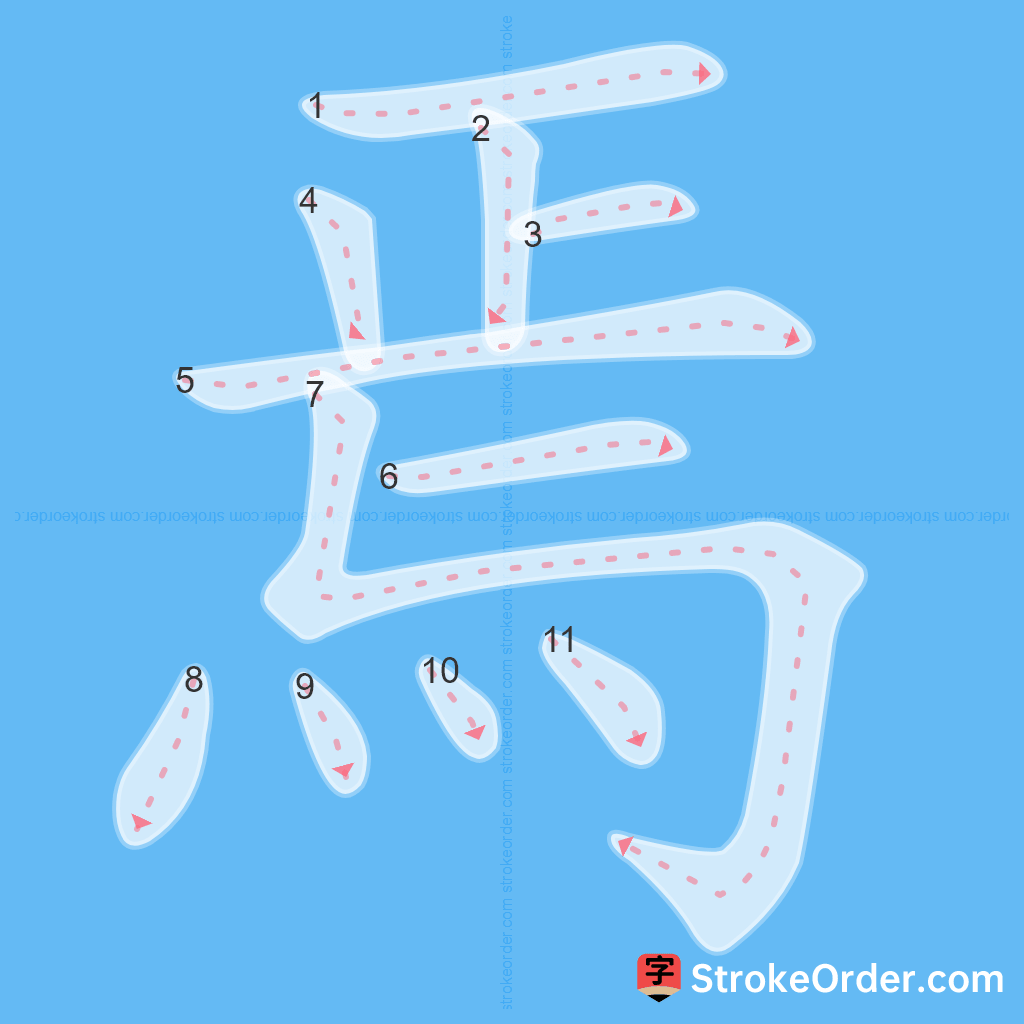
Learn to Write Chinese Characters with Video Tutorials
Watch the video of writing the Chinese character "焉", learn the correct stroke order (笔顺) of the character "焉", and master the standard way of writing the character "焉".
Free Printable Handwriting Practice with Stroke Order: 焉
Printable Writing Practice Worksheet of "焉" in Portrait Orientation (Tian Zi Ge)
Printable Writing Practice Worksheet of "焉" in Landscape Orientation (Tian Zi Ge)
Information of 焉
Pinyin
yān
Radical
灬
Strokes
11 strokes
Usage
★★★★★
Definition
where / how
焉 [yān]
1. 与介词“于”加代词“是”相当。
Equivalent to the preposition "于" and the pronoun "是": 心不在焉 (The heart is not in it.). 不复出焉 (No longer comes out.).
2. 乃,才。
Only, just: 必知乱之所自起,焉能治之。(Must know where chaos arises, only then can it be treated.)
3. 文言疑问词,怎么,哪儿。
Classical Chinese question word, how, where: 且焉置土石?(And where to place soil and stones?)
4. 文言助词。
Classical Chinese particle: 又何戚焉。(What need to grieve then?)
---
焉 [yān]
1. 鸟名 (a kind of bird)
Example: 唐·黄滔《唐城客梦》:旦,北而徂山之曲,乃见苍翠一林,其中则楮烟墨宇,椒枥坎地,群焉胙充,飞而不举。
2. 通“颜”( yán)。额 (forehead)
Example: 《荀子·非相》:身长七尺,面长三尺,焉广三寸,鼻目耳具,而名动天下。(Height is seven feet, face is three feet long, forehead three inches wide, with all features, thus name renowned.)
---
焉 [yān]
1. 表示指示,相当于“之” (it)
Example: 草木无知,叩焉何益? (Plants are ignorant, what use in striking it?)
2. 哪里或那里 (where)
Example: 且焉置土石。(And where to place the soil and stones?)
3. 什么 (what)
Example: 今王公大人骨肉之亲、无故富贵、面目美好者,焉故必知哉? (Why must the rich and noble be known?)
4. 怎么 (which)
Example: 食其禄,焉避其难? (How can one eat their salary but not avoid their troubles?)
5. 兼有介词“于”加代词“此”的语法功能,相当于“于是”、“于此” (so)
Example: 二陵焉。(So there are two tombs.)
---
焉 [yān]
1. 如何 (how)
Example: 如:焉能;焉得;焉敢;焉知;焉用. (How could; how could achieve; how dare; how know; how use.)
2. 于是,就,乃,则 (then).
Example: 《史记》:始皇巡陇西、北地,出鸡头山,过回中,焉作信宫渭南。(The First Emperor toured Longxi and Beidi, passed Jitou Mountain, and thus built the palace south of the Wei River.)
---
于是 (then).
Indicates sequence in ancient Chinese often used with "乃".
---
焉 [yān]
1. 表示结构,用于前置的宾语之后,相当于“之”,“是” (be)
Example: 今王播弃黎老,而孩童焉比谋。(Now the king discards the old Li, yet children plot.)
2. 后缀,表示状态,用于形容词、副词之后,相当于“然”、“样子”
Example: 其心休休焉,其如有容。(His heart is calm, in a state of content.)
3. 用于句中表示停顿,相当于“啊” (ho)
Example: 且以五帝之圣焉而死,三王之仁焉而死… (And thus dies with the sanctity of the Five Emperors, with the benevolence of the Three Kings...)
4. 用于句尾,表示陈述或肯定,相当于“矣”、“呢”
Example: 及至秦之季世,焚《诗》《书》,坑术士,六艺从此缺焉。(When it came to the end of the Qin, burned “Shijing” and “Shu,” buried scholars, and the Six Arts were thus lost.)
5. 用于句尾,表示疑问,相当于“乎”、“吗”
Example: 嗟行之人,胡不比焉? (Alas, those who travel, why do they not compare?)
6. 用于句尾,表示感叹,相当于“呢”、“啊”
Example: 使其中无可欲者,虽无石椁,又何戚焉? (If there’s nothing desirable within, even without a stone coffin, what is there to grieve over?)
Yanqi Hui Autonomous County in Bayingolin Mongol Autonomous Prefecture, Xinjiang 巴音郭楞蒙古自治州[Ba1 yin1 guo1 leng2 Meng3 gu3 Zi4 zhi4 zhou1], Xinjiang
Input Method for 焉
Pinyin
yan1
Wubi
ghgo
Cangjie
mylf
Zhengma
aizu
Four Corner
10327
Unicode
U+7109
Same Pronunciation Characters