盐 Stroke Order
Animated Stroke Order of 盐
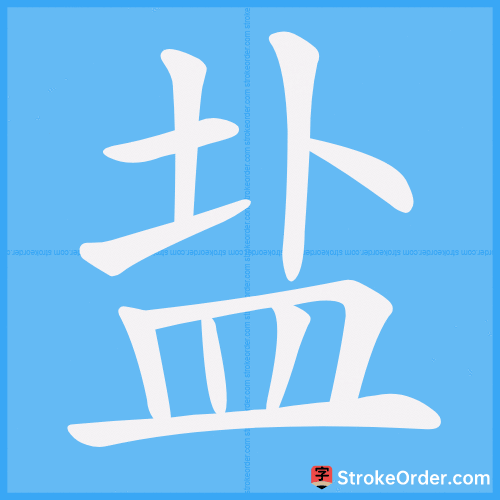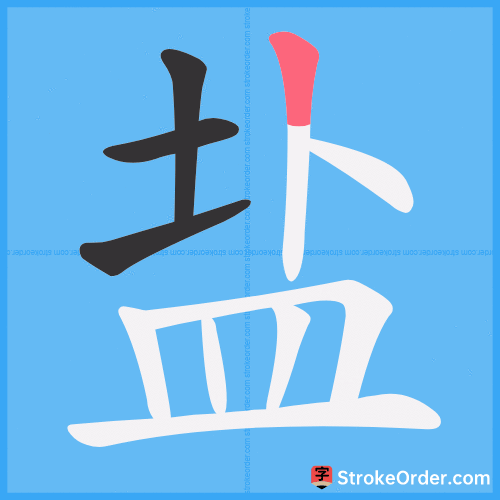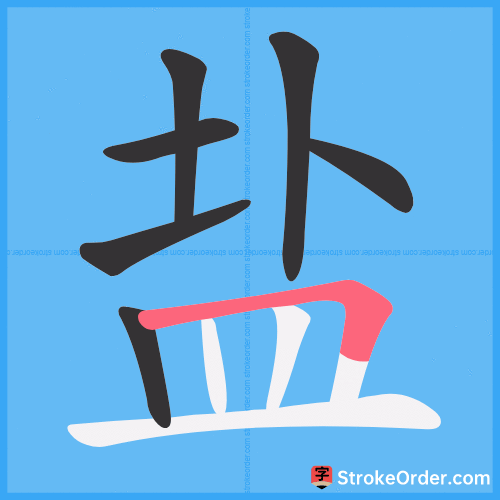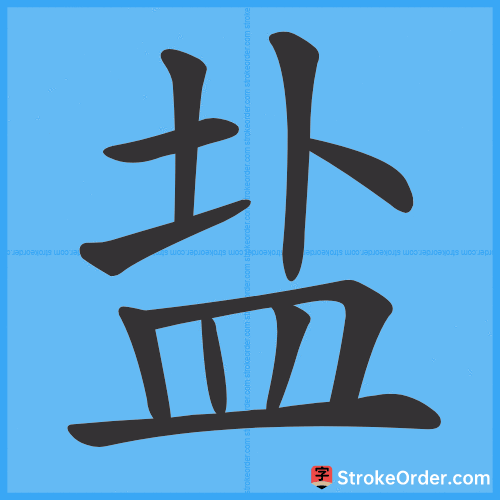
Stroke Order Diagrams for 盐
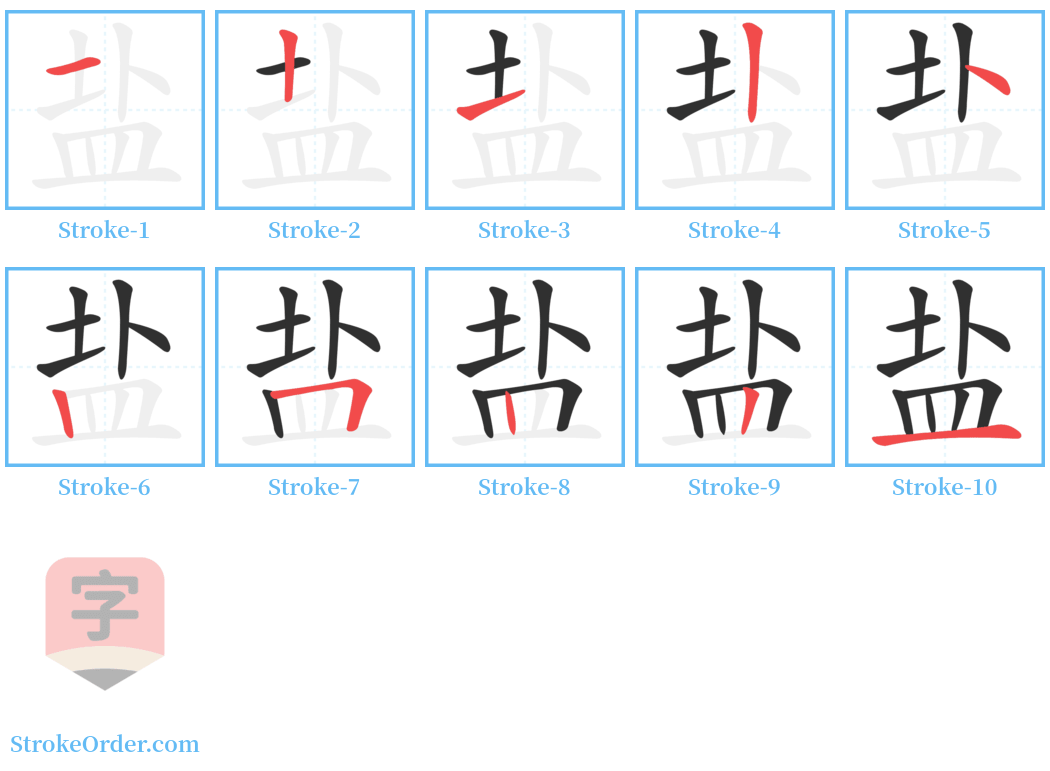
Step-by-Step Handwriting Guide for 盐
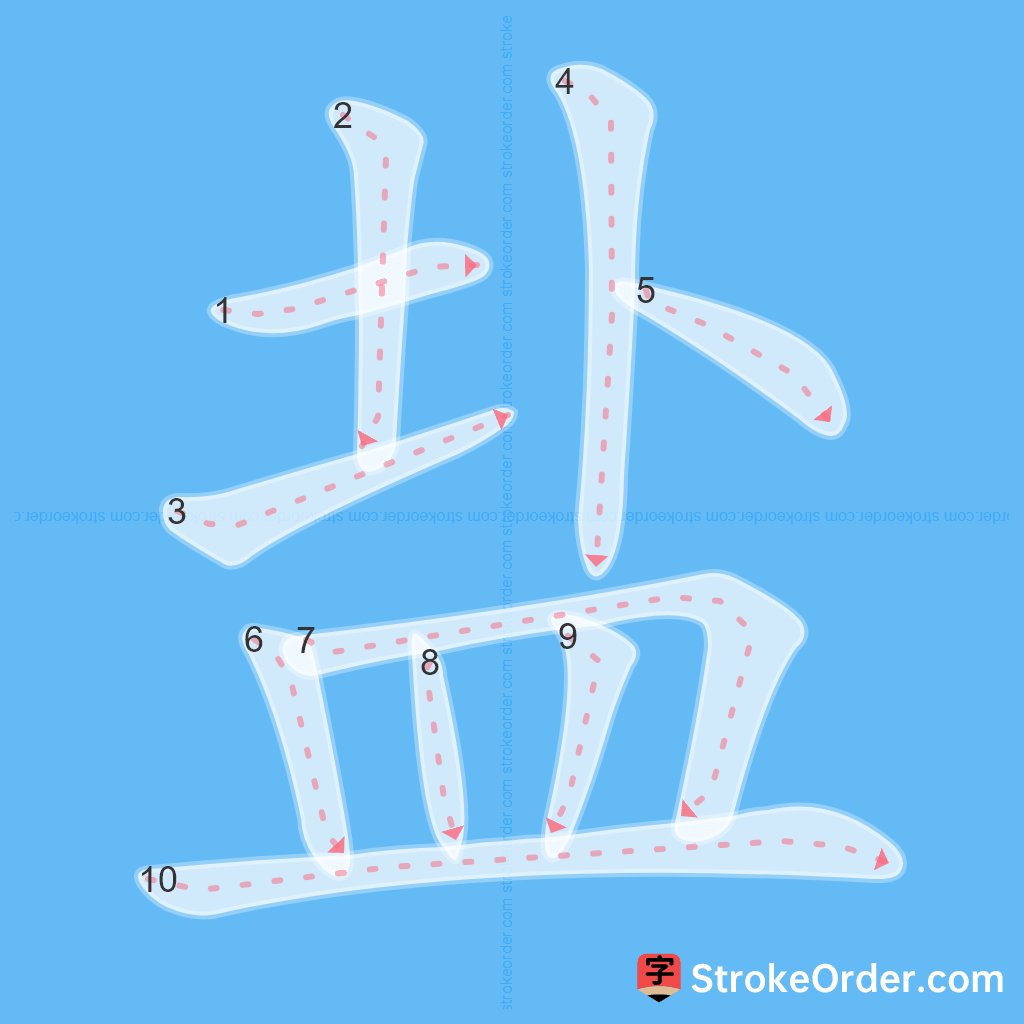
Learn to Write Chinese Characters with Video Tutorials
Watch the video of writing the Chinese character "盐", learn the correct stroke order (笔顺) of the character "盐", and master the standard way of writing the character "盐".
Free Printable Handwriting Practice with Stroke Order: 盐
Printable Writing Practice Worksheet of "盐" in Portrait Orientation (Tian Zi Ge)
Printable Writing Practice Worksheet of "盐" in Landscape Orientation (Tian Zi Ge)
Information of 盐
Pinyin
yán
Radical
皿
Strokes
10 strokes
Usage
★★★★★
Definition
salt
盐 (yán)
[名]
【本义】: 食盐
1. An inorganic compound, a colorless or white crystalline substance with a salty taste, composed of sodium chloride, used for making dyes, glass, soap, etc., also an important seasoning and preservative (includes types such as "sea salt," "lake salt," "well salt," "rock salt").
2. [Salt Acid] A water solution of hydrochloric acid, a basic chemical raw material, widely used in industry and medicine.
3. A compound formed by the neutralization of acids and bases in chemistry.
【引】
1. "Shu·Shuoming" (《书·说命下》): If you prepare the soup, all you need is salt and plum.
2. "Shiji·Huozhiliezhuan" (《史记·货殖列传》): Lu salt lacquer thread.
【例】
1. Salt sauce mouth (to speak unlucky words, which come true).
2. Salt owl (a person who privately trades salt).
3. Salt pound (during the Song Dynasty, salt was calculated in hundreds and thousands of pounds, hence "salt" is referred to as "salt pound").
4. Salt capture division (an official subordinate to the governor who manages salt affairs).
5. Salt ticket law (a system implemented in the Song Dynasty where merchants relied on salt tickets for salt sales, specifically salt monopoly law).
6. Salt fool (a derogatory term for salt merchants).
7. Salt official (present Haining, Zhejiang).
8. Salt office (the government office managing salt laws).
9. Salt laborer (a person working in salt fields).
10. Salt certificate (a document granted by the government to merchants for trading official salt).
11. Salt cart (a cart for transporting salt).
2. A compound composed of metal ions (or ammonium ions NH4+) and acid ions.
3. Salts that contain hydrogen ions are called acidic salts, e.g., ammonium bicarbonate (NH4 HCO3); sodium bisulfate (NaHSO4); potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KH2 PO4).
4. Salts that contain hydroxide ions are called basic salts, e.g., basic copper carbonate (Cu2(OH)2CO3).
5. Salts that do not contain hydroxide or hydrogen ions are called neutral salts, e.g., sodium chloride (NaCl); sodium carbonate (Na2CO3). Additionally, there are complex salts (like alum) and so on.
Input Method for 盐
Pinyin
yan2
Wubi
fhlf
Cangjie
gybt
Zhengma
bilk
Four Corner
43102
Unicode
U+76d0
Same Pronunciation Characters