稀 Stroke Order
Animated Stroke Order of 稀

Stroke Order Diagrams for 稀
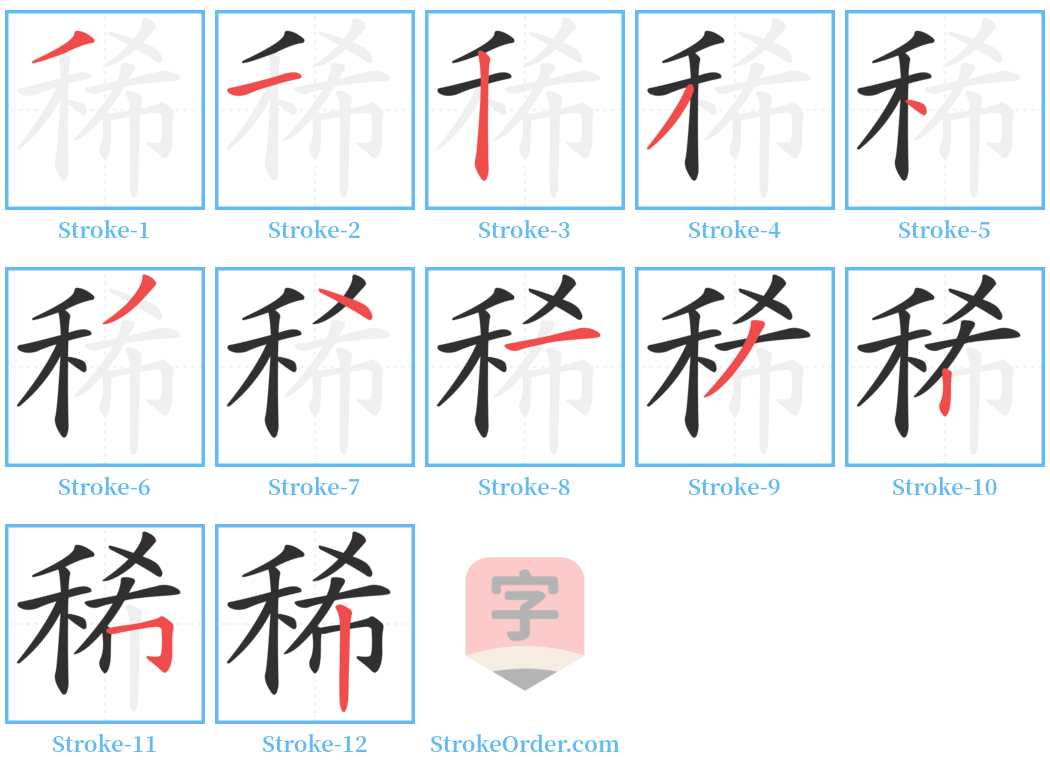
Step-by-Step Handwriting Guide for 稀
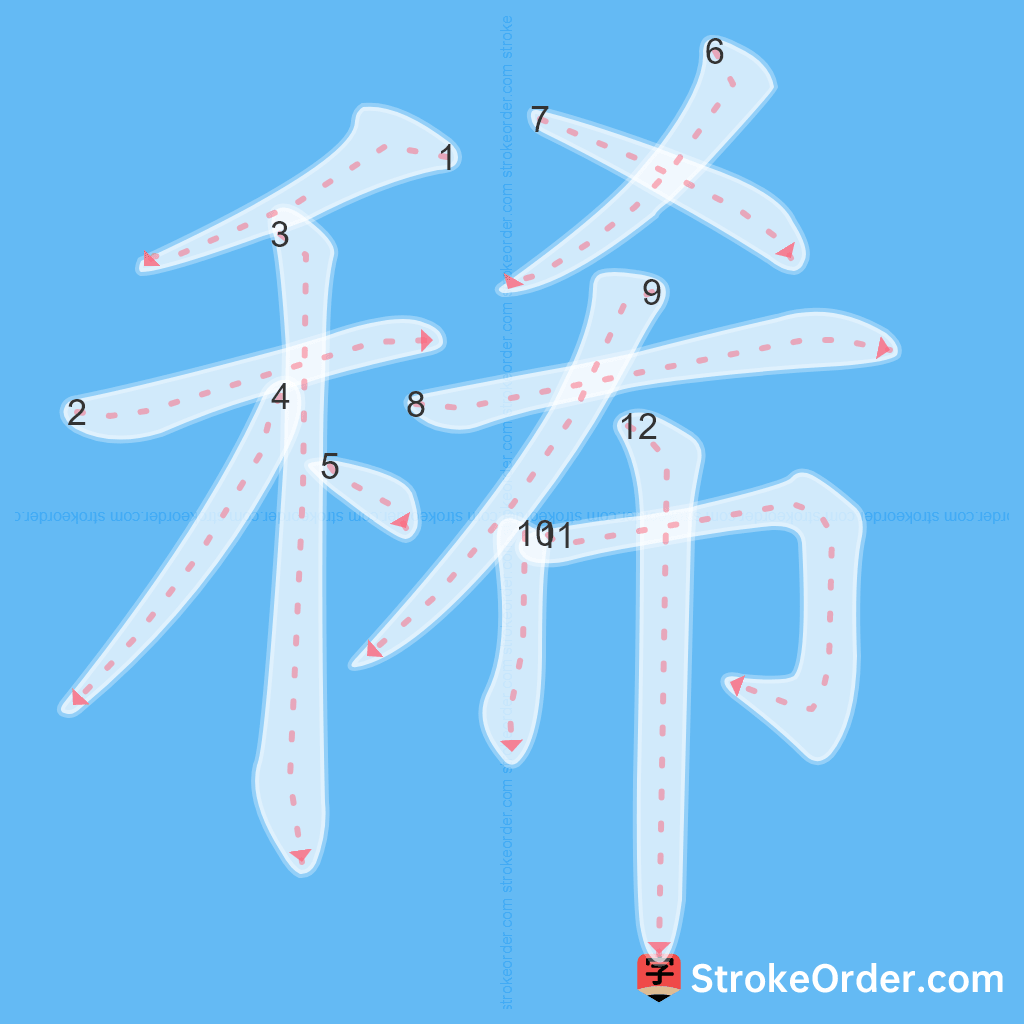
Learn to Write Chinese Characters with Video Tutorials
Watch the video of writing the Chinese character "稀", learn the correct stroke order (笔顺) of the character "稀", and master the standard way of writing the character "稀".
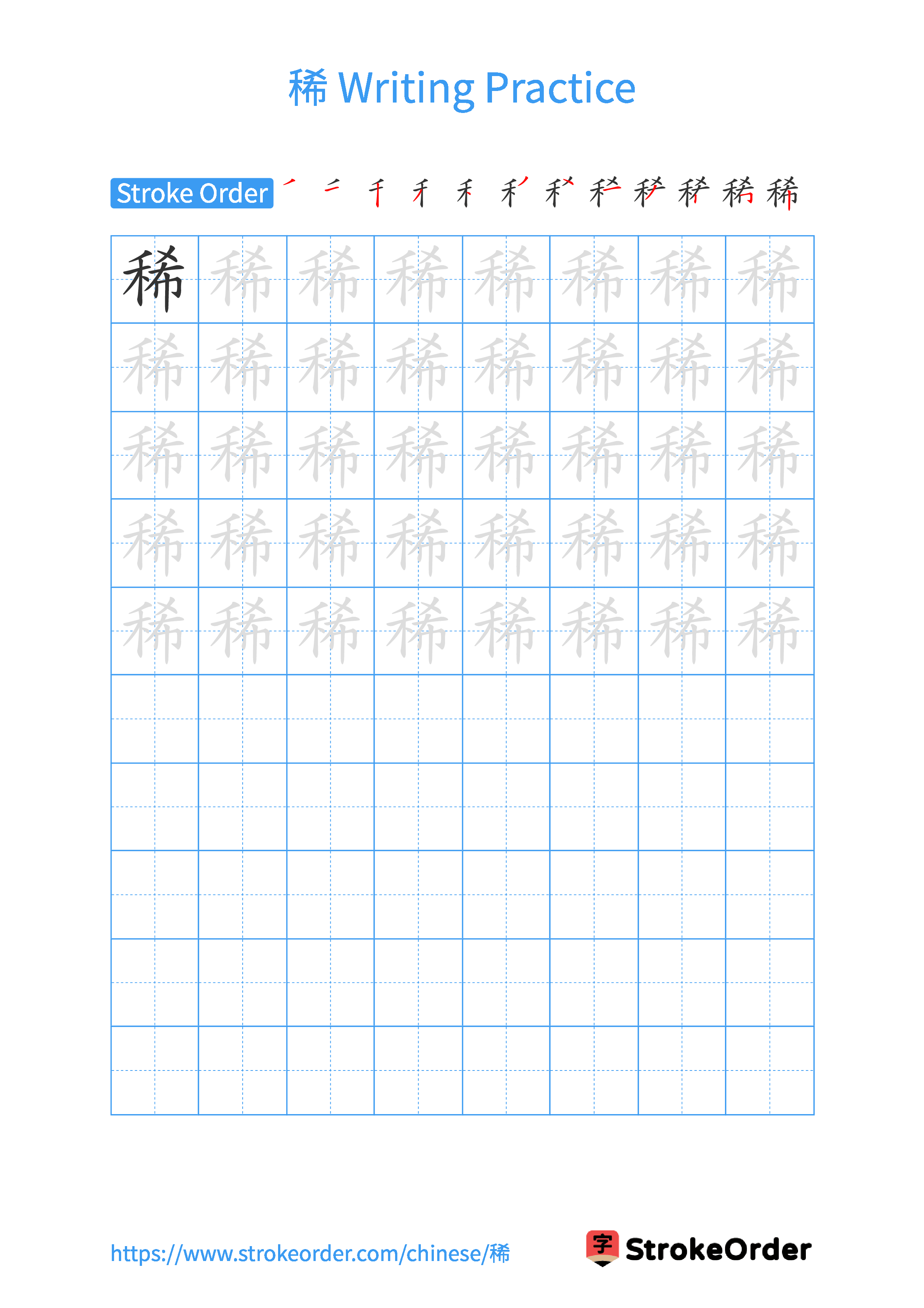
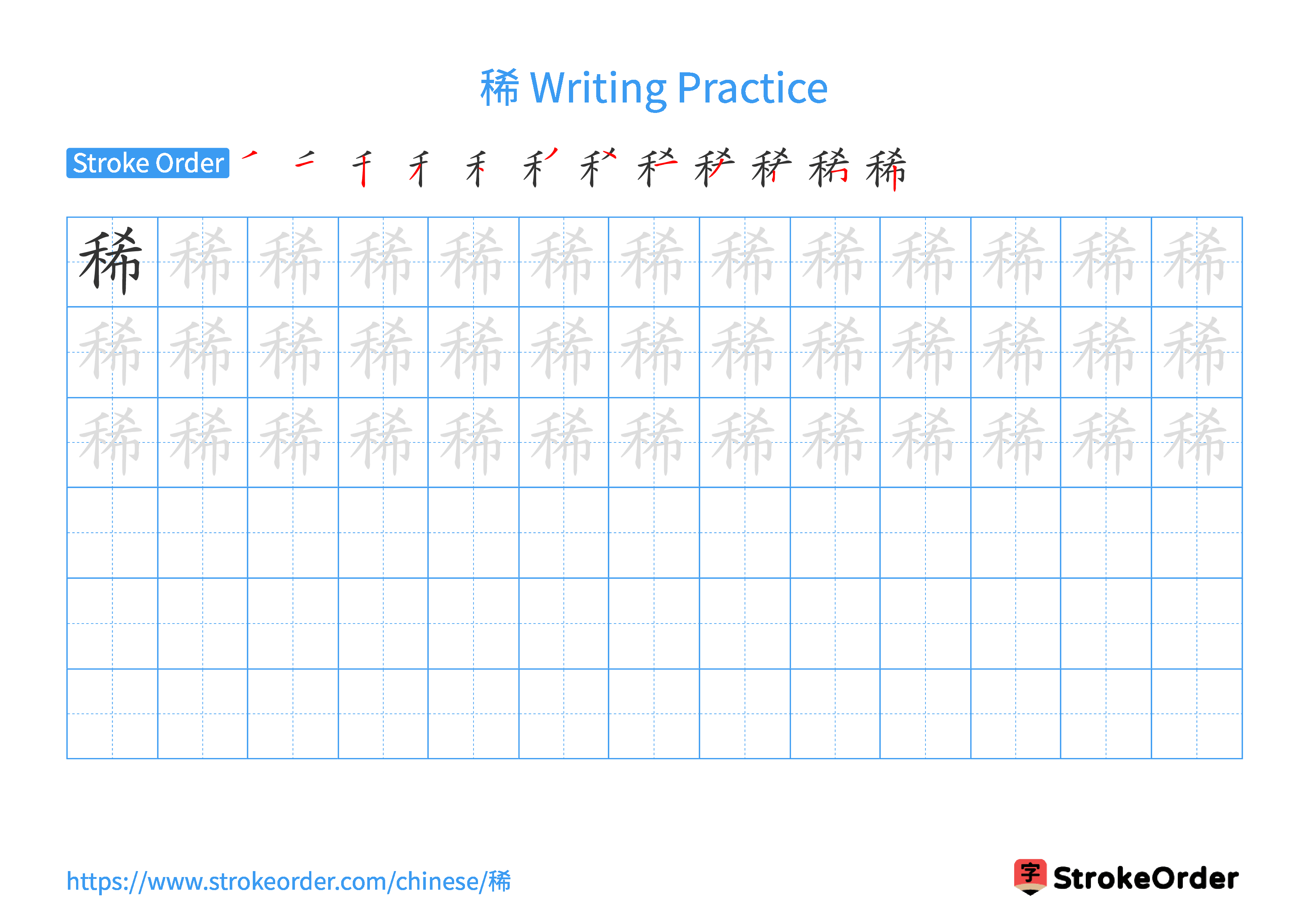
Free Printable Handwriting Practice with Stroke Order: 稀
Printable Writing Practice Worksheet of "稀" in Portrait Orientation (Tian Zi Ge)
Printable Writing Practice Worksheet of "稀" in Landscape Orientation (Tian Zi Ge)
Information of 稀
Pinyin
xī
Radical
禾
Strokes
12 strokes
Usage
★★★★★
Definition
diluted / sparse
稀 [xī]
形 1. Distance between objects is large; sparse, opposite of "dense." Examples: 稀疏 (sparse), 稀落 (scattered), 稀客 (rare guest), 依稀 (faintly).
2. Low concentration; high water content; opposite of "thick." Examples: 稀薄 (thin), 稀料 (diluted material), 稀释 (dilute).
3. Few; not many. Examples: 稀少 (rare), 稀罕 (rare), 稀奇 (unusual), 古稀之年 (the age of seventy).
4. Used in front of adjectives like "rotten" or "loose" to indicate a deep degree. Examples: 稀烂 (very rotten), 稀碎 (very broken), 稀松 (very loose).
副 Very; extremely. Used to describe a high degree.
Example: 稀不相干 (not related at all); 稀秃湿 (soaked); 稀醉 (very drunk).
引 1. From Xu Shen's "Shuowen Jiezi": 稀 means sparse.
2. From Cao Cao's "Short Song Line": 月明星稀 (the moon and stars are sparse).
3. From Du Fu's "Tired Night": 重露成涓滴,稀星乍有无 (heavy dew forms into drops, sparse stars appear and vanish).
4. From Tao Qian's "Return to the Garden": 种豆南山下,草盛豆苗稀 (planting beans at the foot of the south mountain, the grass is lush but the bean sprouts are sparse).
Example: 稀棱挣 (sparse appearance), 稀撒撒 (scattered), 稀星 (sparse stars), 稀零零 (extremely sparse), 稀稀落落 (appearance of sparsity; looks deserted).
(onom.) rustling sound / sound of rain or of sth falling down / in disorder / completely smashed / badly battered / broken to pieces
Input Method for 稀
Pinyin
xi1
Wubi
tqdh|trdh
Cangjie
hdkkb
Zhengma
mfgl
Four Corner
24927
Unicode
U+7a00
Same Pronunciation Characters