籍 Stroke Order
Animated Stroke Order of 籍
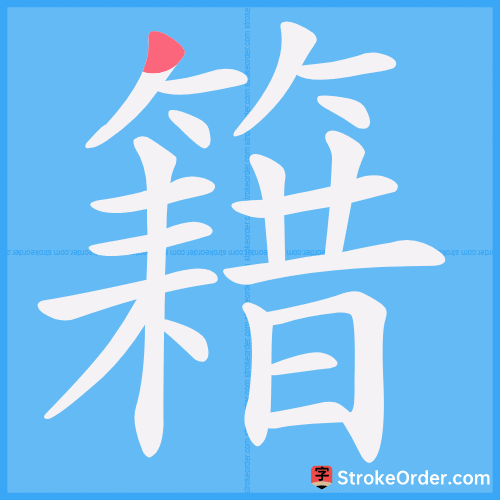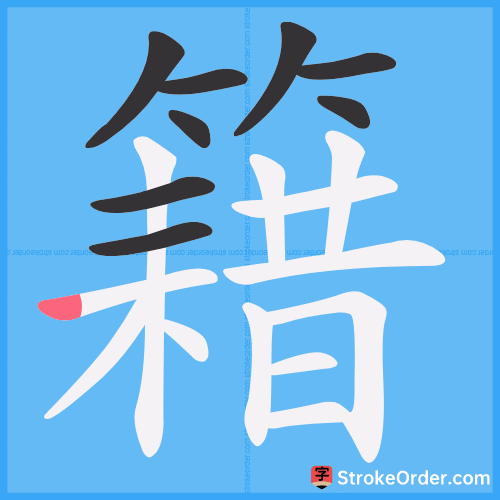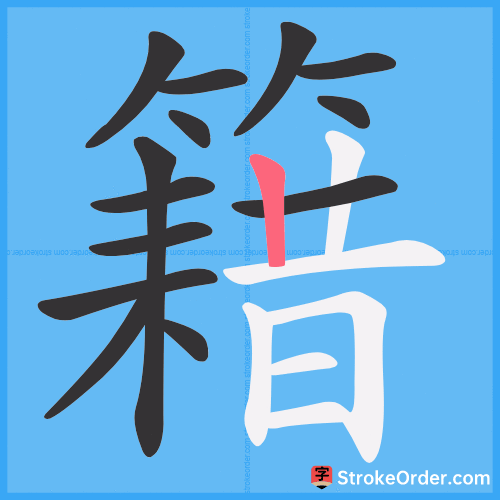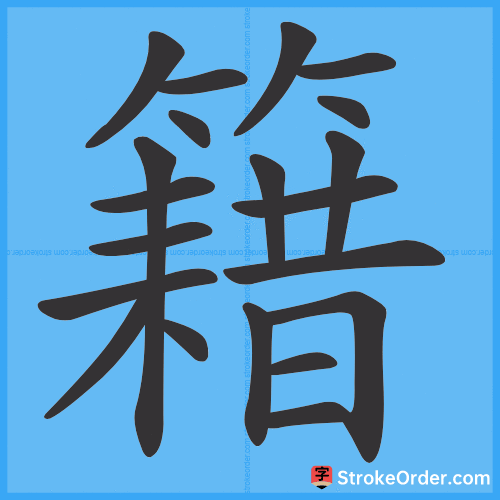
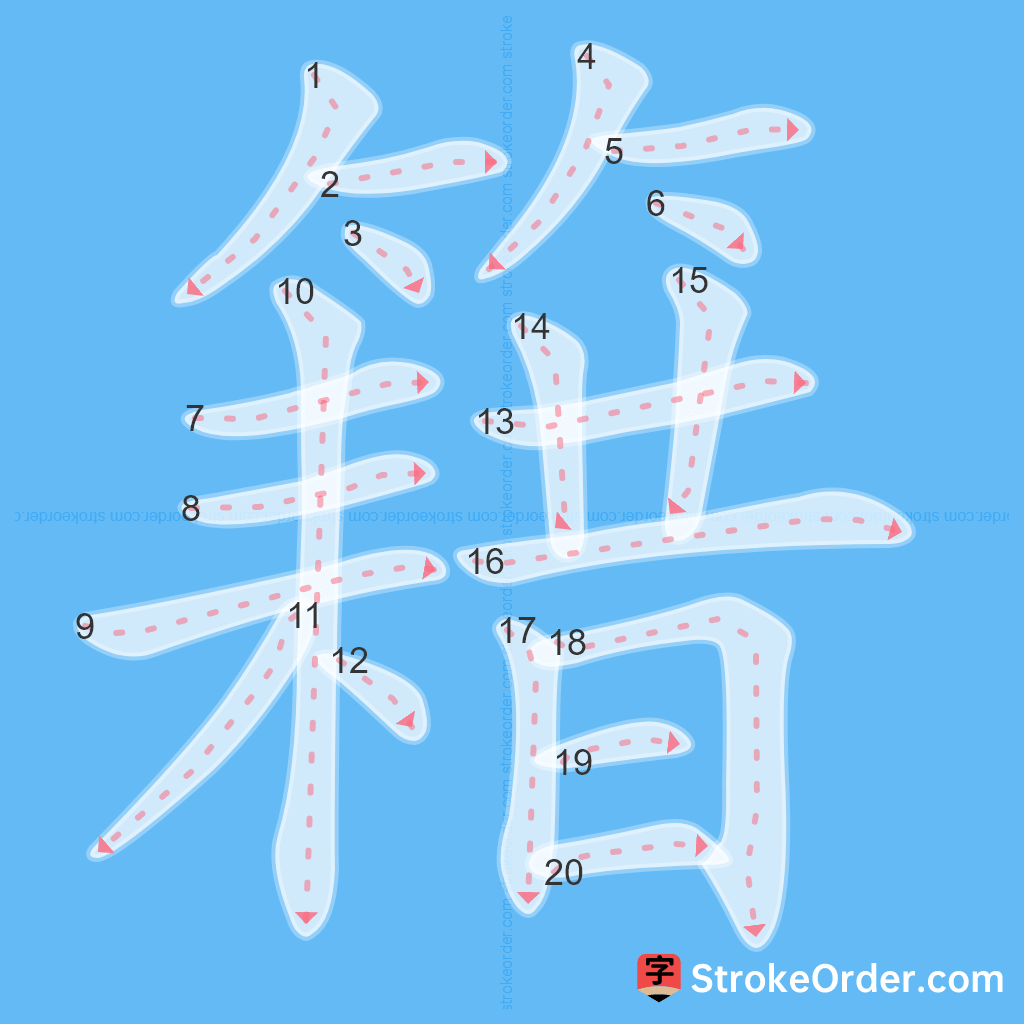
Stroke Order Diagrams for 籍

Step-by-Step Handwriting Guide for 籍
Learn to Write Chinese Characters with Video Tutorials
Watch the video of writing the Chinese character "籍", learn the correct stroke order (笔顺) of the character "籍", and master the standard way of writing the character "籍".
Free Printable Handwriting Practice with Stroke Order: 籍
Printable Writing Practice Worksheet of "籍" in Portrait Orientation (Tian Zi Ge)
Printable Writing Practice Worksheet of "籍" in Landscape Orientation (Tian Zi Ge)
Information of 籍
Pinyin
jí
Radical
竹
Strokes
20 strokes
Usage
★★★★★
Definition
(surname) / record / register / native place
籍 [jí]
名
1 书,书册:古籍,书籍,经典,典籍。
(Book; register: ancient books, publications, classics, canons.)
2 登记隶属关系的簿册;隶属关系:籍贯,户籍,国籍,学籍。
(Register of membership; membership: native place, household registration, nationality, student registration.)
3 登记:籍没(mò),籍吏民。
(Registration: to record and confiscate; to register officials and citizens.)
4 征收:籍田。
(To levy: to levy taxes on farmland.)
5 〔~~〕❶形容纷扰很大;❷形容名声很大;❸形容纵横交错的样子。
(Descriptive: 1. To describe chaos; 2. To describe great fame; 3. To describe interwoven appearances.)
6 古代各种捐税的统称。
(General term for various taxes in ancient China.)
动
1 登记:登记籍贯名字;登记征用民夫;籍田(古代天子亲耕之田)。
(To register: to record hometown names; to register labor; to register farmland (the land personally cultivated by the emperor in ancient times).)
2 没收入官:如:籍配,籍没和充军。
(To confiscate: e.g., to annex and conscript.)
3 假借,通“借”。
(To use as a pretext; to make use of.)
形
杂乱,如:狼籍。
(In disorder, e.g., a mess.)
**Note:** The character 籍 has different meanings and uses in Chinese, ranging from a book or register to aspects of identity and taxation. It can also describe order or chaos in context.
Input Method for 籍
Pinyin
ji2
Wubi
tdij|tfsj
Cangjie
hqda
Zhengma
mcek
Four Corner
88961
Unicode
U+7c4d
Same Pronunciation Characters