古 Stroke Order
Animated Stroke Order of 古
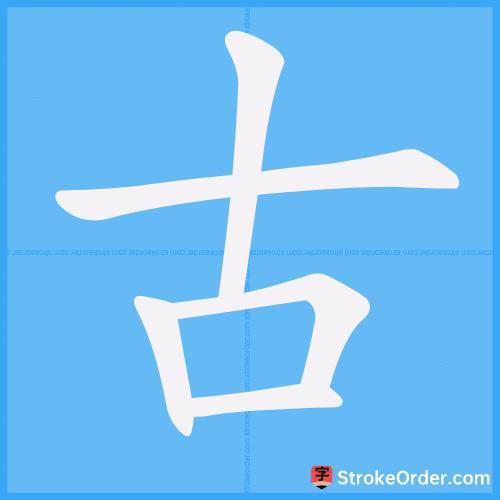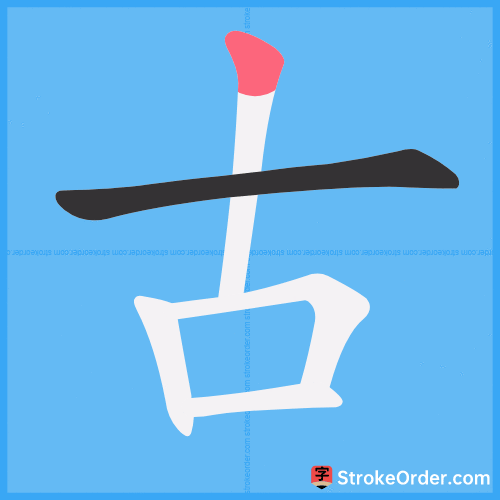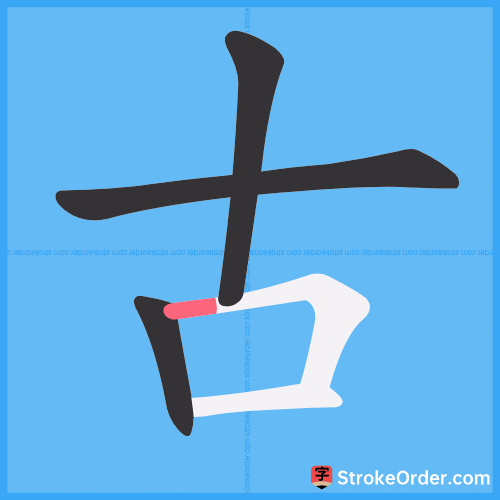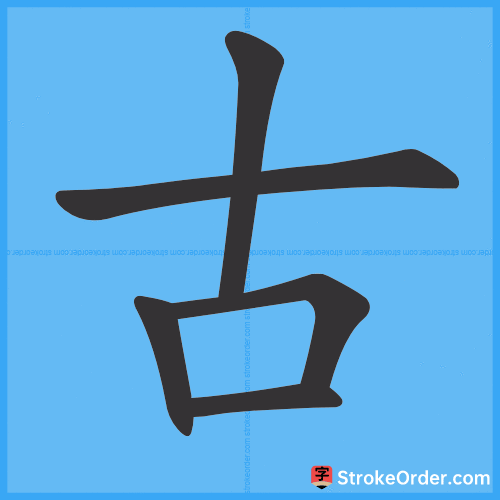
Stroke Order Diagrams for 古
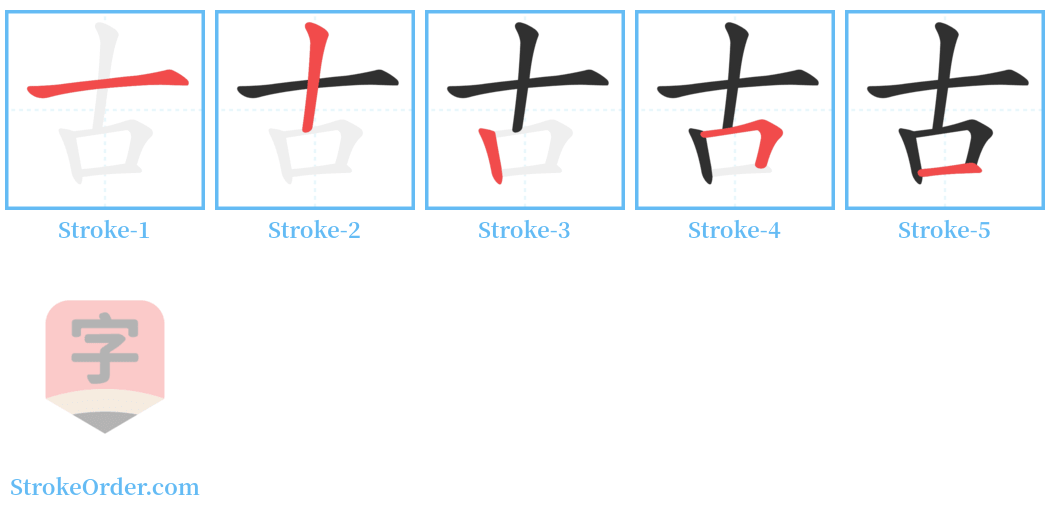
Step-by-Step Handwriting Guide for 古
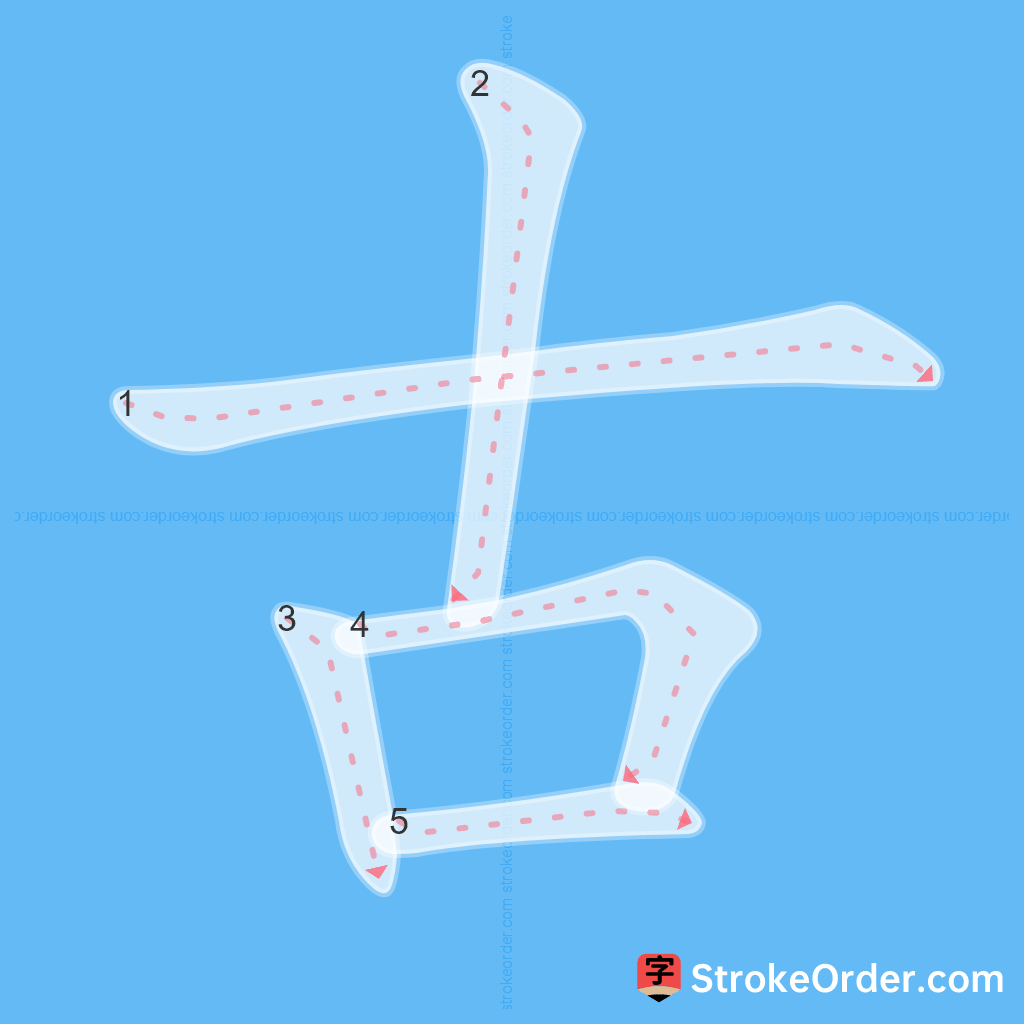
Learn to Write Chinese Characters with Video Tutorials
Watch the video of writing the Chinese character "古", learn the correct stroke order (笔顺) of the character "古", and master the standard way of writing the character "古".
Free Printable Handwriting Practice with Stroke Order: 古
Printable Writing Practice Worksheet of "古" in Portrait Orientation (Tian Zi Ge)
Printable Writing Practice Worksheet of "古" in Landscape Orientation (Tian Zi Ge)
Information of 古
Pinyin
gǔ
Radical
口
Strokes
5 strokes
Usage
★★★★★
Definition
ancient / old
古 [gǔ]
Noun:
1. (Ancient times) Refers to a long time ago, past; opposite of "now": 古代 (ancient era), 古稀 (the term for a person in their seventies, derived from Du Fu's "Life's Seventy is Rare"), 古典 (ancient texts), 古风 (ancient customs), 古训 (ancient teachings), 古道 (a. refers to ancient principles; b. ancient simplicity; c. old pathways).
2. Abbreviation for ancient-style poetry: 五古 (five-character ancient poem), 七古 (seven-character ancient poem).
3. A surname.
Meaning:
1. Same as the original meaning (ancient times).
2. Objects from ancient times, particularly the texts and traditions of ancient sages; ancient rules and literature.
3. The ancients.
4. Heaven.
5. Abbreviation for ancient-style poetry.
6. Abbreviation for Cuba.
7. Onomatopoeia; e.g., 古剌剌 (sound of a flag fluttering or a whip cracking); 古鲁鲁 (referring to a rolling sound of objects or liquid); 古都都 (describing the sound of continuously flowing water).
Adjective:
1. Ancient; age-old - used to refer to things that have existed for a long time.
2. Simple; unadorned.
3. Strange; unconventional; obstinate.
4. Old; former.
Examples:
1. 古文明 (ancient civilization), 古王朝 (ancient dynasty), 古堡 (ancient fortress), 古渡 (ancient ferry), 古礼 (ancient ceremonial rites).
2. 古穆 (ancient, simple, and solemn); 古健 (ancient robust strength).
3. 古董 (obstinate person); 古涩 (referring to difficult-to-read old texts).
4. 古法 (old methods).
Bo Gu (1907-1946), Soviet-trained Chinese Communist, journalist and propagandist, 1930s Left adventurist, subsequently rehabilitated, killed in air crash
cunning / queer / an eccentric person with a streak of the fox in him / sly and capricious / tricky service
Input Method for 古
Pinyin
gu3
Wubi
dghg
Cangjie
jr
Zhengma
edj
Four Corner
40600
Unicode
U+53e4
Same Pronunciation Characters